[ad_1]
Do you know that EVs want as much as six occasions extra minerals than typical vehicles?
EVs are mineral-intensive and are pushing up demand for vital battery metals. Based on the Worldwide Power Company (IEA), lithium, nickel, and cobalt demand is predicted to develop from 10%-20% to over 80% by 2030.
As international locations around the globe pledge to go all-electric by 2035 and 2040, Visible Capitalist’s Tessa Di Grandi and Zack Aboulazm talk about whether or not now we have sufficient mineral provide for EV demand?
Elements similar to geopolitical focus of sources, high quality of supplies, mining business lead occasions, and environmental elements will collectively decide whether or not now we have the minerals we’d like.
Let’s check out how vital minerals are affected.
|
Mineral |
Constraints |
|---|---|
|
Copper |
Copper mines presently in operation are nearing their peak, affected by reserve exhaustion, whereas ore high quality in older mines is declining. South American and Australian mines are positioned in areas the place water availability could be scarce. |
|
Nickel |
There are a selection of rising considerations associated to larger CO2 emissions and waste disposal. Nickel high quality must be excessive (Class 1) for EV batteries. Most nickel within the international provide chain is unusable for EVs. |
|
Cobalt |
The Democratic Republic of Congo and China account for round 70% of manufacturing. 90% of cobalt produced is a by-product of nickel and copper, making new provide topic to the event of those mines. |
|
Uncommon Earth Parts |
Issues surrounding damaging environmental credentials in processing operations. The worth chain from mining to processing and magnet manufacturing is geographically concentrated in China. |
|
Lithium |
The world might face extreme lithium shortages as early as 2025. Lithium mines that began operations between 2010-2019 took a mean of 16.5 years to develop. China accounts for 60% of world manufacturing and greater than 80% of lithium hydroxide. Over 50% of lithium mines are positioned in areas that undergo water shortages. |
Recycling is a partial answer to alleviate vital mineral provide however will fall in need of assembly the excessive ranges of demand till across the 2030s.
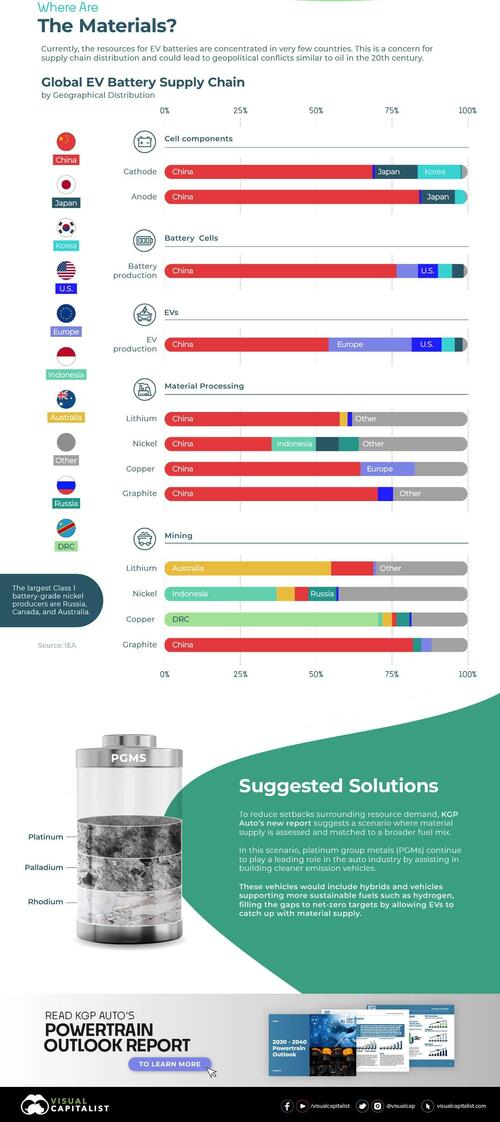
The EV Provide Chain
At present, the sources for EV batteries are concentrated in only a few international locations. This focus is an rising concern for provide chain distribution.
China is house to greater than half of the world’s lithium, cobalt, and graphite processing and refining capability, in addition to three-quarters of all lithium-ion battery manufacturing capability.
Europe accounts for greater than one-quarter of worldwide EV meeting, however house to little or no of the availability chain, with the area’s cobalt processing share accounting for 20% of the combo.
In the meantime, each Korea and Japan management a large portion of the downstream provide chain after uncooked materials processing. Korea accounts for 15% of worldwide cathode materials manufacturing capability. Japan produces 14% of cathode and 11% of anode materials.
The US accounts for simply 10% of EV manufacturing and seven% of battery manufacturing capability.
Instructed Options
To scale back setbacks surrounding useful resource demand, KGP Auto’s new report recommends that materials provide is accessed and matched to a broader gasoline power combine.
On this state of affairs, platinum group metals (PGMs) proceed to play a number one position within the auto business by aiding in constructing cleaner emission autos.
These autos assist extra sustainable fuels similar to hydrogen, filling the gaps to net-zero targets by permitting EVs to meet up with materials provide.
Learn KGP Auto’s Powertrain Outlook Report to study extra.
Loading…
[ad_2]