[ad_1]
By Peter Claeys, Visiting Professor on the Division of Economics of the Faculty of Europe, and the Universiteit Gent, Béatrice Dumont, Professor of economics at Sorbonne College Paris and Director of the Division of Economics on the Faculty of Europe, Martin Larch, Head of Secretariat at European Fiscal Board, and Wouter van der Wielen, Economist at European Funding Financial institution. Initially printed at VoxEU.
Main financial downturns have left essential scars within the path of financial growth, regardless of forceful and common makes an attempt to assist combination demand. This column summarises discussions at a latest workshop on scarring results and techniques to avert or minimise them. Fiscal coverage can play an essential position in limiting hysteresis – a time period coined within the Nineteen Eighties – notably by selling authorities and personal funding. Nevertheless, the political economic system of fiscal policymaking usually trades off long-term advantages for short-term features.
The World Disaster rekindled a dialogue that has absorbed macroeconomists and policymakers for many years. Within the aftermath of main financial downturns, financial exercise doesn’t return to its pre-crisis pattern. In different phrases, main downturns depart ‘scars’ – a catchy expression for detrimental supply-side results. Blanchard et al. (2015), Ball (2014), Martin et al. (2015) and Cerra et al. (2021) are notably distinguished examples of latest research documenting the entrenched sample. The foundations of their work had been laid a very long time in the past, within the early Nineteen Eighties, when Nelson and Plosser (1982) confirmed that cycles weren’t happening round steady however fairly variable tendencies.
Other than coping with lasting results on financial output, essentially the most bothering a part of scarring is the (un)effectiveness of financial insurance policies. Scarring results appear to materialise even within the face of forceful reactions each on the financial and the fiscal aspect. Issues is probably not so clear within the wake of smaller cyclical swings when policymakers could not at all times agree concerning the alternative to lean towards the wind. When giant shocks hit, nevertheless, there’s often a enough sense of urgency within the political system of any democratic nation to design, deliberate, and dispense essential fiscal assist packages. And nonetheless, scarring results persist, and the one-million-dollar query is why.
Whereas there could also be a number of forces at play, one appeared to be of explicit significance and was on the centre of a workshop held on the Faculty of Europe in Bruges on 23-24 November 2022, particularly, funding, and public funding particularly.[1] The concept for the workshop was born after three of the 4 authors of this column took a better have a look at the position of fiscal coverage after main financial downturns in 20+ OECD international locations for the reason that Nineteen Seventies (Larch et al. 2022). Our empirical evaluation supplied clear proof that though fiscal coverage can mitigate scarring results, policymakers didn’t give sufficient consideration to authorities funding; they favoured fiscal assist with short-lived results on output (see Determine 1). Over time, the sequence of forceful fiscal responses with short-lived output results adopted by scarring results gave rise to sustainability points.
Determine 1 Stylised information of main financial downturns in 26 OCED international locations, together with 14 EU Member States, 1970–2020
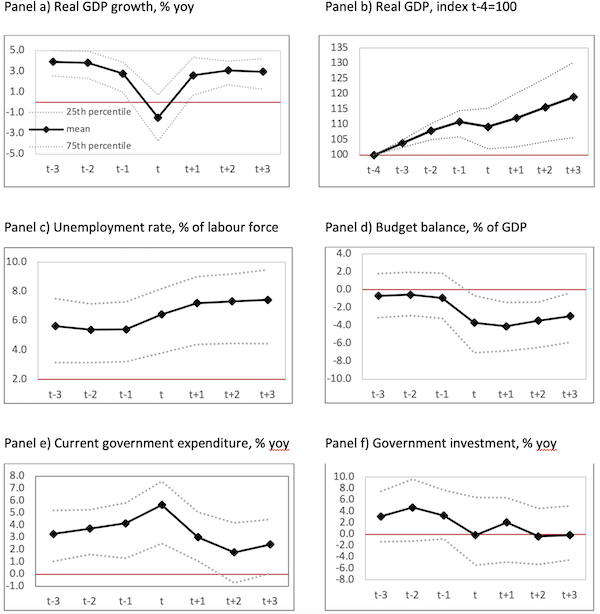
Observe: Behaviour of actual GDP and monetary variables within the three years earlier than and after main financial downturns.
Supply: Larch et al. (2022)
Scarring Results Are Pervasive and Sizeable, Particularly After Main Financial Downturns
Quantifying the scarring results of main financial downturns isn’t a simple train, as there is no such thing as a observable counterfactual. On high of our work (Larch et al. 2022), which broadly adopted the method by Blanchard et al. (2015), the workshop on the Faculty of Europe featured a second paper assessing the significance and measurement of scarring results. Making use of a novel technique specializing in the distribution of development charges earlier than, throughout and after recessions, Drehmann et al. (2022) convincingly corroborated the truth that extreme contractions led to extremely persistent detrimental development results. Smaller contractions didn’t have such an impression. Of explicit notice, Drehmann et al. (2022) didn’t discover assist for optimistic hysteresis, i.e. robust expansions don’t appear to trigger persistent above-trend development.
The pervasiveness of scarring results would and may appeal to restricted consideration if the consequences had been small in measurement, however the reverse was true. According to the broader literature within the subject, the proof introduced on the workshop confirmed that the lasting shortfall of financial exercise and/or development after main downturns may very well be surprisingly large. Within the OECD pattern we used, the typical annual scarring impact three to seven years after a significant financial downturn amounted to 1 ½ – 2% of the pre-recession pattern. Utilizing a really comparable pattern, Drehmann et al. (2022) discovered that for the 20% most extreme contractions, the drop in GDP is, on common, 4.25% in ten years.
On high of confirming the empirical significance of scarring after main financial downturns, the workshop additionally supplied insights into the particular mechanisms that generate lasting results on financial exercise or development. Two invited keynote audio system – Andrea Roventini of Scuola Superiore Sant’Anna in Pisa and Valerie Cerra, Assistant Director on the IMF – supplied essential insights. Specializing in state-of-the-art normal equilibrium fashions, Andrea Roventini showcased a collection of channels that may generate extended recessions by connecting development and enterprise cycle idea as in Dosi et al. (2010), Dosi et al. (2017) and Dosi et al. (2018). These fashions couple endogenous development (pushed by innovation) with combination demand (pushed by consumption and funding) so insurance policies that assist funding can mitigate and even avert scarring results.
Based mostly on a complete overview of the empirical literature on how economies and financial insurance policies behave after recessions – a literature to which she has made essential contributions –Valerie Cerra underscored the significance for policymakers to behave rapidly and aggressively in response to a recession, particularly by addressing the supply-side damages that may in any other case ensue.
The Coverage Response to Scarring
The scarring results revealed by the empirical literature and confirmed by the papers introduced on the workshop beg essential questions for policymakers, most significantly: how can scarring results be mitigated?
Within the early days, the prevailing concept was that any fiscal growth supporting combination demand would diminish or forestall scarring results. Nevertheless, the persistence of scarring within the face of main fiscal expansions forged critical doubts over this politically interesting notion. We discovered restricted proof that standard fiscal demand stimuli centred on present expenditure mitigate scarring. Whereas estimates of short-run fiscal multipliers had been sizeable, particularly in unhealthy financial occasions, they tended to reverse pretty rapidly and even turned detrimental within the medium time period. Therefore, handing out revenue assist via greater present spending or just preserving beforehand adopted expenditure plans on observe when the economic system tanked didn’t assist tackle structural or supply-side points triggered by extreme financial downturns. Against this, we confirmed that authorities funding may mitigate scarring results, however within the overwhelming majority of instances, the main target of fiscal policymakers within the wake of main downturns remained on the brief time period, i.e. public funding programmes weren’t the standard response.
Tervala and Watson (2022) corroborated the significance of public funding by taking a really cautious have a look at a particular and extremely profitable coverage intervention. An area education funding program mixed with a labour market intervention in Australia between 2009-12 was discovered to provide very excessive multipliers weighing towards any doubtlessly lasting results the fallout of the Nice Disaster had on GDP in numerous elements of the nation. Within the context of European areas, Brasili et al. (2022) discovered that native public funding correlated positively with personal funding, particularly in financial downturns. This highlighted the position of native public funding in stimulating personal funding and, in flip, financial exercise extra usually. Based on Brasili et al. (2022), the funding with the very best return was to be present in schooling and coaching, R&D, but in addition infrastructure.
In his opening speech, Maarten Verwey, Director-Common of Financial and Monetary Affairs on the European Fee, pressured how the European coverage response to the Covid-19 pandemic marked a major change in comparison with earlier crises by banking on the potential advantages of presidency funding and structural reforms. In post-WWII historical past, the Restoration and Resilience Facility was certainly a uncommon and commendable instance of a significant coverage initiative taken within the wake of a significant downturn that aimed to strengthen medium and long-term development prospects fairly than producing a sugar rush of combination demand.
The credibility of the coverage framework can also play a task in addressing supply-side results. Particularly, if fiscal guidelines grow to be extra credible, this may produce a wave of optimism that helps will increase in combination demand, together with funding. A paper by Betti et al. (2022) confirmed that intervals of hysteresis may very well be dodged by the adoption of fiscal guidelines that reinstate the sustainability of public debt.
Within the Financial and Financial Union, the place financial coverage can’t at all times stabilise idiosyncratic shocks, fiscal threat sharing can mitigate the tendency for financial divergence by offsetting extended recessions on the regional stage, as Hauptmeier et al. (2022) argue. Following an identical line of reasoning and the extra normal reasoning by Obstfeld (2016), Cimadomo et al. (2022) discovered that fiscal risk-sharing supported development largely over the long term, particularly in poorer areas.
Conclusions
Lengthy criticised as gradual and ill-timed, the coverage responses to the World Disaster and the Covid-19 pandemic initiated a reassessment of fiscal coverage as a stabilisation instrument. On the similar time, there’s ample proof that main financial downturns produce lasting results on actual GDP regardless of lively fiscal coverage intervention. Because of this, fairly a couple of superior economies ended up accumulating excessive public debt with out fostering long-term development prospects.
The workshop held finish November final 12 months on the Faculty of Europe in Bruges introduced collectively specialists and policymakers to take a recent have a look at the lasting results of main financial downturns and learn how to tackle them. The papers introduced on the occasion clearly present that coverage responses can mitigate scarring results however should be extra focused in the direction of provide aspect channels. Particularly, there was rising proof that authorities funding can dampen or avert lasting output results. In distinction, greater present expenditure – the favoured coverage response in observe – would assist demand within the brief time period whereas heightening sustainability points in the long term.
In sum, fiscal policymakers face an important trade-off between short-term stabilisation and long-term sustainability: favouring the previous will exacerbate the latter, whereas specializing in sustainability via greater funding could value well-liked assist. The trade-off is fraught with political economic system points however might be overcome as evidenced by the EU’s Restoration and Resilience Facility.
Footnotes
[1] The workshop was collectively organised by the Economics Division of the Faculty of Europe, the European Funding Financial institution and the Secretariat of the European Fiscal Board.
[ad_2]
