[ad_1]
Germany’s financial system shrank greater than anticipated within the fourth quarter in line with revised figures, elevating doubts over the flexibility of Europe’s greatest financial system to flee recession and get better swiftly from its vitality disaster.
Excessive inflation drove sharp falls in German shopper spending and funding in buildings and equipment within the last quarter of 2022, the federal statistics workplace mentioned on Friday, which led to a 0.4 per cent contraction in gross home product from the earlier quarter.
That’s the second downward revision in Germany’s newest GDP figures prior to now month. Initially Destatis estimated the financial system had stagnated, earlier than saying a 0.2 per cent fall in fourth-quarter output in its flash estimate on the finish of January.
The largest quarterly decline within the nation’s GDP because the begin of 2021 outstripped economists’ expectations, in line with a ballot by Reuters. The contraction, coupled with latest upward revisions in German and eurozone estimates for inflation, dealt a blow to hopes that Europe will swiftly rebound from the fallout of Russia’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine one yr in the past.
Current surveys of companies and customers have painted a extra upbeat image of Europe’s financial system at the beginning of this yr, nevertheless, suggesting it could show extra resilient than anticipated after a light winter helped to decrease gasoline costs and avert fears of vitality shortages.
“Trying forward, the latest upturn within the surveys is constructive, however we doubt that the financial system has sufficient momentum to keep away from one other fall in first-quarter GDP, and in consequence, a technical recession,” mentioned Claus Vistesen, an economist at analysis group Pantheon Macroeconomics. A recession is outlined as two consecutive quarters of falling output.
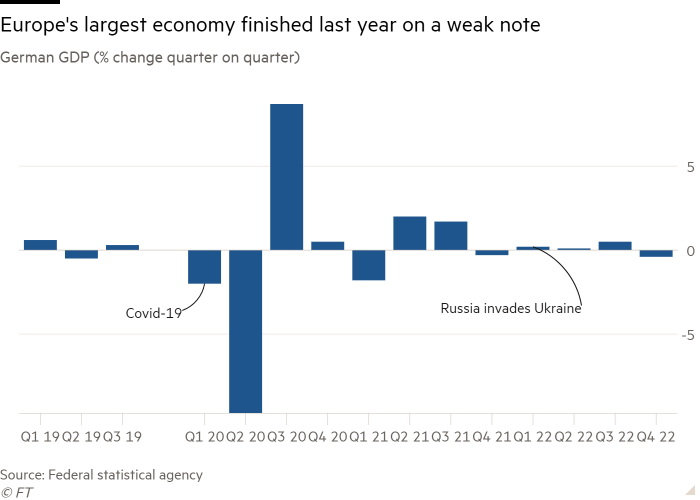
German funding in development and tools, resembling equipment and autos, fell 2.5 per cent quarter on quarter. The nation’s commerce surplus was weaker than anticipated, as exports fell 1 per cent and imports had been down 1.3 per cent. Nevertheless, authorities spending rose 0.6 per cent.
“The continued sturdy value will increase and the continued vitality disaster weighed on the German financial system on the finish of the yr,” Destatis mentioned, including that this was “notably noticeable in non-public shopper spending”, which fell 1 per cent within the three months to the tip of December.
Family spending dropped after the federal government ended some assist measures, resembling a reduction on gasoline and a subsidised €9-a-month prepare ticket, it mentioned, regardless that Berlin paid most individuals’s gasoline payments in December and plans to cap them this yr.
The figures “present that the sharp rise in vitality costs has noticeably slowed down the financial system, regardless of the federal government’s in depth support measures”, mentioned Ralph Solveen, an economist at German lender Commerzbank. He added that rate of interest rises by the European Central Financial institution had been “prone to have had an impression on the development sector specifically”.
Analysis group GfK mentioned on Friday that its German shopper confidence index rose to minus 30.5, up from minus 33.8 within the earlier month, barely under economists’ expectations and nicely under the constructive scores of lower than two years in the past.
[ad_2]