[ad_1]

The Nationwide Institute of Requirements and Know-how (NIST) introduced that ASCON is the successful bid for the “light-weight cryptography” program to search out the most effective algorithm to guard small IoT (Web of Issues) units with restricted {hardware} assets.
Small IoT units have gotten more and more widespread and omnipresent, utilized in wearable tech, “good residence” purposes, and so forth. Nevertheless, they’re nonetheless used to retailer and deal with delicate private info, similar to well being knowledge, monetary particulars, and extra.
That mentioned, implementing a typical for encrypting knowledge is essential in securing individuals’s knowledge. Nevertheless, the weak chips inside these units name for an algorithm that may ship strong encryption at little or no computational energy.
“The world is shifting towards utilizing small units for plenty of duties starting from sensing to identification to machine management, and since these small units have restricted assets, they want safety that has a compact implementation,” said Kerry McKay, a pc scientist at NIST.
“These algorithms ought to cowl most units which have these kinds of useful resource constraints.”
ASCON was chosen as the most effective of the 57 proposals submitted to NIST, a number of rounds of safety evaluation by main cryptographers, implementation and benchmarking outcomes, and suggestions acquired throughout workshops. The entire program lasted for 4 years, having began in 2019.
NIST says all ten finalists exhibited distinctive efficiency that surpassed the set requirements with out elevating safety issues, making the ultimate choice very onerous.
ASCON was finally picked because the winner for being versatile, encompassing seven households, power environment friendly, speedy on weak {hardware}, and having low overhead for brief messages.
NIST additionally thought of that the algorithm had withstood the check of time, having been developed in 2014 by a group of cryptographers from Graz College of Know-how, Infineon Applied sciences, Lamarr Safety Analysis, and Radboud College, and successful the CAESAR cryptographic competitors’s “light-weight encryption” class in 2019.
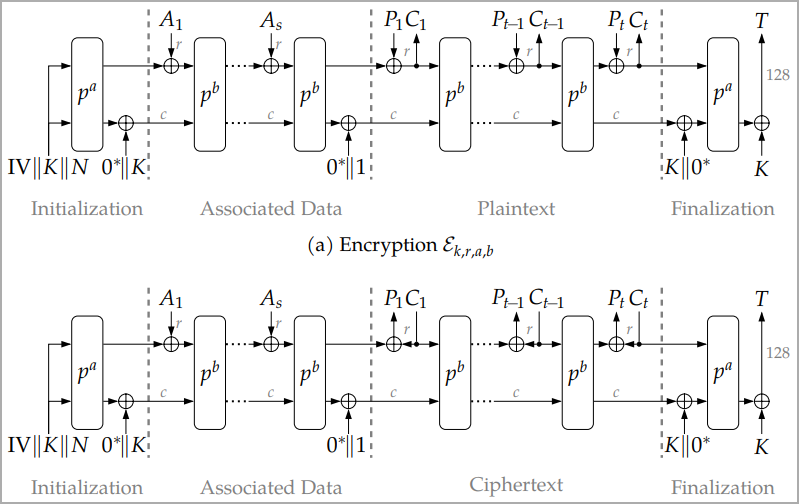
Two of ASCON’s native options highlighted in NIST’s announcement are AEAD (Authenticated Encryption with Related Information) and hashing.
AEAD is an encryption mode that gives confidentiality and authenticity for transmitted or saved knowledge, combining symmetric encryption and MAC (message authentication code) to stop unauthorized entry or tampering.
Hashing is an information integrity verification mechanism that creates a string of characters (hash) from distinctive inputs, permitting two knowledge trade factors to validate that the encrypted message has not been tampered with.
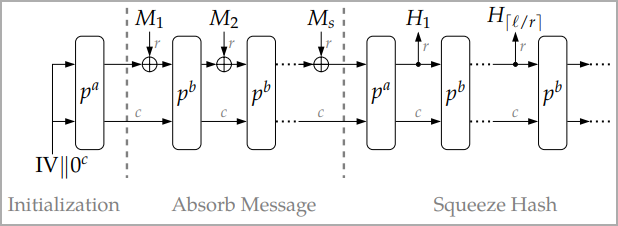
NIST nonetheless recommends the AES method for AEAD and SHA-256 for hashing; nonetheless, these are unsuitable for smaller, weaker units.
Regardless of ASCON’s light-weight nature, NIST says the scheme is highly effective sufficient to supply some resistance to assaults from highly effective quantum computer systems at its customary 128-bit nonce. Nevertheless, this isn’t the aim or function of this customary, and light-weight cryptography algorithms ought to solely be used for shielding ephemeral secrets and techniques.
NIST treats post-quantum cryptography as a separate problem, operating a special program for creating quantum-resistant requirements, and the trouble has already yielded its first outcomes.
For extra particulars on ASCON, test the algorithm’s web site, or learn the technical paper submitted to NIST in Could 2021.
[ad_2]